In recent years, there has been significant development in 3D printing technology, which has resulted in the availability of various printing processes for creating items. Fused Deposition Modeling, sometimes known as FDM, and Resin printing are two very common processes.

In this article, we will examine the distinctions between the two approaches, as well as their respective benefits and drawbacks, and then determine which approach is likely to be the superior option for a variety of uses. 3D Printing FDM vs. Resin, let’s find out everything about them.
3D Printing FDM vs. Resin: Differences Between the Two
There are many differences when it comes to 3D printing FDM vs. Resin. Let’s start with FDM first, shall we?
1. What is Fused Deposition Modeling, aka FDM?
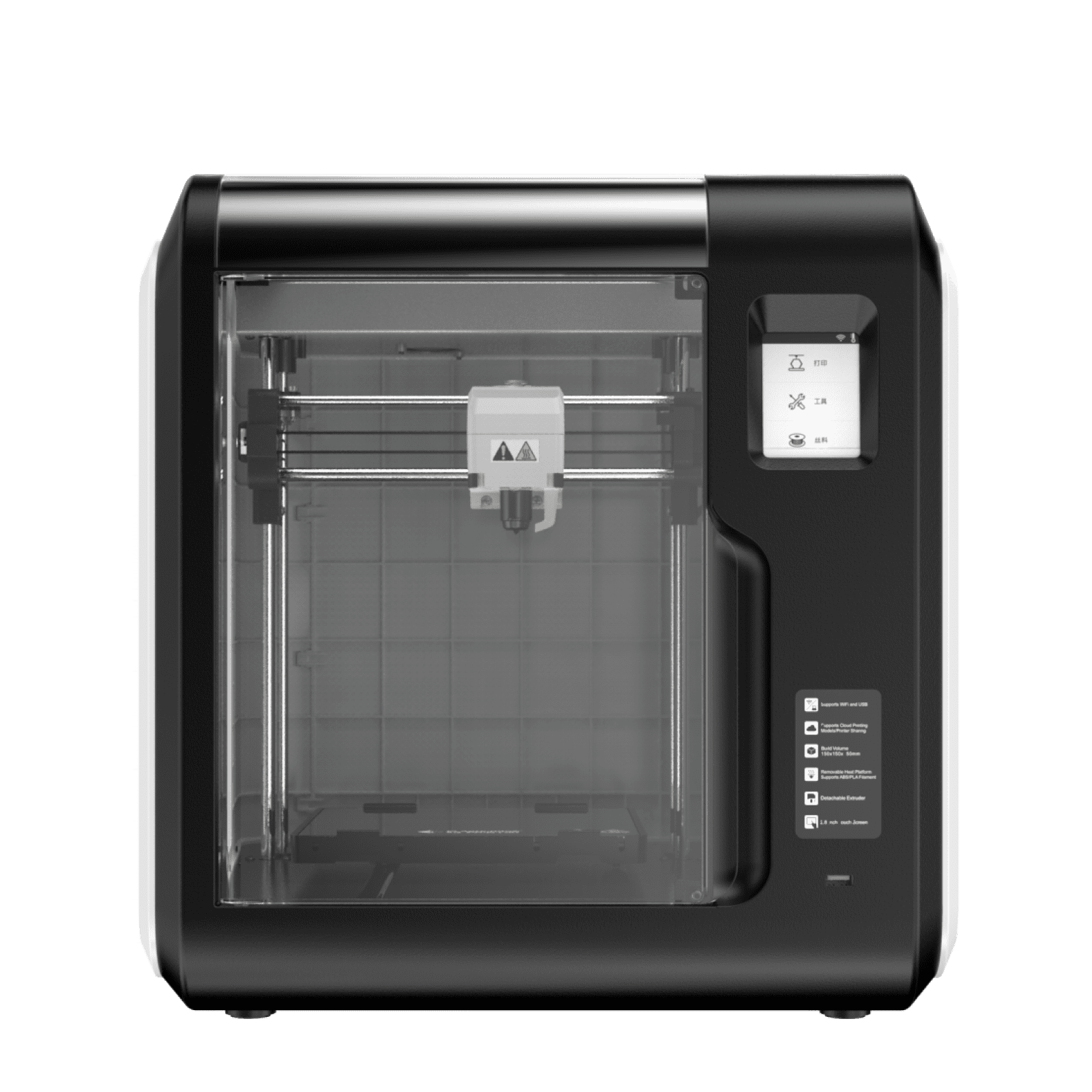
One of the most common three-dimensional printing types is fused deposition modeling or FDM for short. This technique involves melting a thermoplastic material and forcing it through a nozzle in order to build up an item layer by layer. In most cases, the material is introduced into the machine in the form of a filament.
This filament is then heated before being deposited onto a build platform. Because of its cheap cost, simplicity of use, and capacity to generate functioning components, fused deposition modeling (FDM) is one of the most extensively used technologies for three-dimensional printing.
FDM 3D Printers are available in a wide variety of sizes and configurations, ranging from tiny machines designed for hobbyists to big industrial systems. These 3D Printers are also reasonably affordable.
3D Printing FDM vs. Resin: when talking about those, they are capable of printing in a wide range of materials, such as PLA, ABS, PETG, Nylon, and TPU, among others. Because FDM printing is also reasonably rapid compared to other 3D printing technologies, it is particularly well-suited for prototyping and manufacturing in small batches. There are a lot of educational uses of these printers.

The fact that layer lines may be seen on the finished product is among the most significant drawbacks associated with FDM printing. Prints made using FDM have a distinct "stepped" look, which may be challenging to smooth out. Warping is another issue that may occur with FDM prints, which is particularly problematic when trying to print huge, flat things.
This challenge may be overcome by using a heated build platform, making use of an adhesive for the print bed, and maintaining temperature control with precision.
2. What Is Resin Printing?
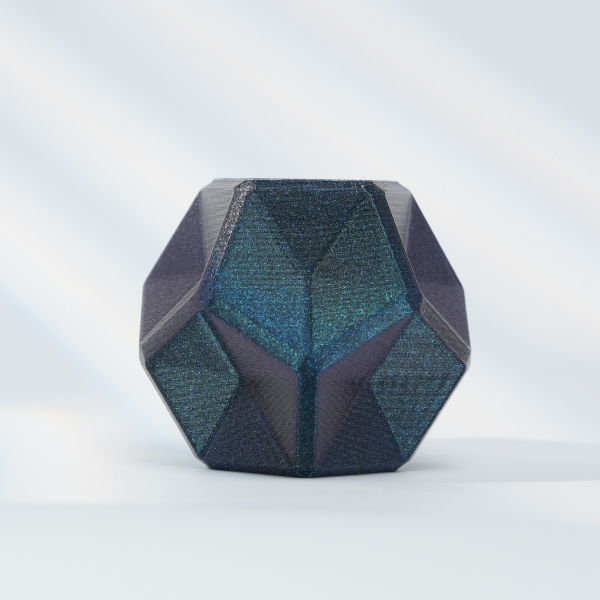
Resin printing, which is also known as stereolithography (SLA), is a type of 3D printing that creates items by building them up layer by layer using liquid Resin and a source of ultraviolet light. The ultraviolet radiation cures the Resin, resulting in the formation of a solid component.
Printing in Resin allows for producing exceptionally smooth and precise components with exquisite features and a high level of detail. The cost of Resin 3D Printers is often more than that of FDM 3D Printers; nevertheless, Resin 3D Printers can also create better-quality components.
Printing with Resin is well suited for producing tiny, complex components that require attention to detail and precision. In addition, Resin prints do not have the apparent layer lines that FDM prints have, making them ideal for use in producing completed goods.
What do you think about 3D Printing FDM vs Resin: Which is more cost-effective? Unfortunately, the high cost of the materials required for Resin printing is one of its most significant drawbacks. In addition to being costlier than filament, the Resin has a much shorter shelf life. Consumers have a lot of different varieties to choose from.

Prints made with Resin must also undergo post-processing since, after printing, they must be cleaned and cured. Because the Resin is a liquid, the printing process may also result in a dirty environment because the liquid Resin might leak or spill if it is not handled correctly.
3D Printing FDM vs. Resin: Which Is Better?
The particular needs of the application in question heavily influence the choice between FDM printing and Resin printing. When it comes to the creation of practical components that do not need a high degree of detail or a flawless finish, FDM printing is the method of choice.
In addition, FDM prints are more robust than Resin prints and can sustain greater wear and tear. In addition, when it comes to 3D Printing FDM vs. Resin, the FDM 3D Printers are more readily accessible and simpler to use than their Resin-based counterparts.
On the other hand, printing with Resin is well suited for producing intricately detailed miniature components that need high precision and flat surfaces. Because Resin prints do not have layer lines that can be seen, they are an excellent choice for use in the production of completed goods and industrial and professional uses.
Resin 3D Printers also have the ability to construct exceedingly detailed and complicated forms, the likes of which would be extremely challenging, if not impossible, to make with FDM printing.
3D Printing FDM vs. Resin: Conclusion
Summing the 3D Printing FDM vs. Resin, FDM printing and Resin printing are two common types of 3D printing, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Resin printing is more suited for the creation of tiny components, while FDM printing is great for the creation of functional parts in a rapid and easy manner.