3D printing can be a thrilling experience, but it's not without its challenges. From print quality issues to filament jams, and bed adhesion problems to firmware errors, troubleshooting is a crucial skill for any 3D printing enthusiast.
With the right troubleshooting skills, you can confidently diagnose and fix common 3D printer issues. That’s why we’ve gone the extra mile to write this troubleshooting guide article - from understanding the root causes of problems to implementing effective solutions.
Say goodbye to failed prints and hello to successful 3D printing with this comprehensive guide in hand!
Common 3D Printer Issues and How to Troubleshoot Them
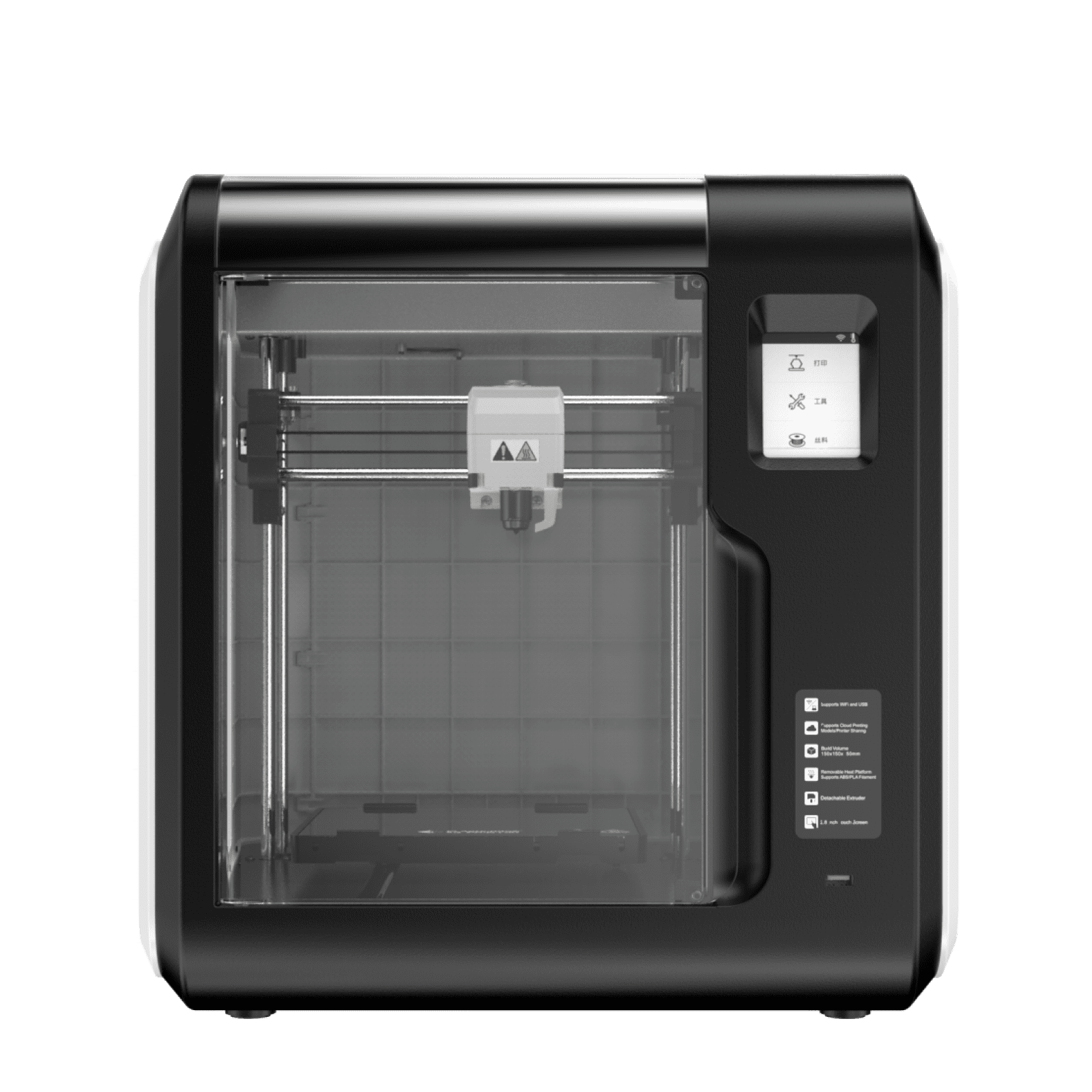
1. FDM 3D Printer Common Issues and How to Troubleshoot Correctly
Troubleshooting Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) 3D printers can be challenging, but with the right approach, many issues can be resolved. Here are some common FDM 3D printer issues and troubleshooting tips:
● Filament jams: Filament jams can occur in the extruder or the hot-end, resulting in failed prints or printer errors. Clear any debris or filament from the extruder gear, nozzle, and hotend.

Adjust the retraction settings, filament tension, and nozzle temperature to prevent filament jams.
● Extrusion problems: Issues such as under-extrusion or over-extrusion can affect print quality. Check that the filament is loaded properly, the extruder gear is clean and gripping the filament properly, and the extruder motor is functioning correctly.
Adjust the filament tension, nozzle temperature, and print speed to optimize extrusion.
● Stringing and oozing: Stringing occurs when the printer leaves unwanted strands of filament between printed parts, and oozing happens when the nozzle drips or leaks filament during print pauses or movements.
Adjust retraction settings, nozzle temperature, and print speed to reduce stringing and oozing. Cleaning the nozzle and using a nozzle wipe or prime tower can also help.
● Print not sticking to the bed: If your print is not adhering to the print bed, it could result in a failed print. Make sure the print bed is clean and level.
If needed, use a print bed adhesive, such as a glue stick or hairspray, to improve bed adhesion. Adjust the print bed height and nozzle gap to ensure proper first-layer adhesion.
● Warping and curling: Warping occurs when the edges of a print lift or curl are due to uneven cooling, improper bed temperature, or insufficient bed adhesion. Use a heated bed or a print bed adhesive, and ensure proper bed leveling and nozzle height.
Consider using a brim or raft to improve print stability and reduce warping.
● Uneven layers or misaligned prints: Issues with the Z-axis can result in uneven layers or misaligned prints. Check for any loose belts, worn out or misaligned Z-axis rods, and binding or debris in the Z-axis mechanism.
Calibrate the Z-axis steps per millimeter (Z-steps) and check the Z-end-stop position to ensure accurate layer height and print alignment.
● Print not completing: If your printer fails to complete, it could be due to a variety of issues, such as power interruptions, loose connections, or even incorrect print settings.
Check all connections, power supply, and print settings to ensure they are properly configured. Consider using a UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) to protect against power interruptions.
● Firmware or software issues: Outdated or incorrect firmware or software can result in printing problems.
Make sure your printer's firmware and software are up-to-date and compatible with your printer model and settings. Resetting or re-flashing the firmware, calibrating the printer, or using different slicing settings can help resolve software-related issues.
Pro tip: Consider getting yourself a good FDM 3D printer with multiple connectivity options. These multiple connectivity options will enable you to easily import files, and update your 3D printer’s software and firmware.

1. Resin-Based 3D Printers (LCD and DLP Technologies)
Troubleshooting resin-based 3D printers can be challenging, as they have their own unique set of issues compared to Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) printers. Here are some common resin-based 3D printer issues and troubleshooting tips:
● Resin contamination: Resin can become contaminated with debris, dust, or cured resin, which can affect print quality and printer performance. Regularly clean the resin vat, and resin tank, and build the platform.
Use a fine-mesh filter or sieve when pouring resin back into the bottle to remove debris. Avoid using contaminated resin in the printer to prevent print quality issues.
● Printer not curing resin properly: Resin needs to be properly cured to ensure the final print is fully hardened and cured. Check the UV light intensity, exposure time, and curing settings to ensure optimal curing.
Consider using a UV light meter to measure the light intensity and calibrate the curing settings accordingly.
● Print not adhering to the build platform: Resin prints need to adhere properly to the build platform to avoid print failures. Ensure that the build platform is clean and level.
Use a compatible resin-compatible build platform adhesive, such as a resin-compatible glue or adhesive sheet, to improve adhesion. Adjust the build platform height and leveling to ensure proper first-layer adhesion.
● Failed or incomplete prints: Resin prints can fail or be incomplete due to various reasons, such as incorrect curing settings, insufficient resin, printing too fast, power loss, etc.
Check and adjust the curing settings, resin level, and print speed to ensure optimal print quality. Consider using a higher-quality resin and optimizing curing settings to reduce print failures. Also, consider using a UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) to protect against power interruptions.
● Printer errors or malfunctions: Resin-based 3D printers can experience errors or malfunctions, such as failed motors, sensors, or electronics. Check for any error messages, flashing lights, or abnormal noises.
Refer to the printer's user manual or manufacturer's support for troubleshooting and resolving printer errors.
Pro tip: Consider getting yourself a good resin-based 3D printer from a reputable manufacturer. One of the things you should look out for in customer reviews is how helpful and responsive the company’s customer support is.
2. Wax-Based 3D Printers
Wax-based 3D printers are used in various applications, such as jewelry making, dental, and casting. However, like any other type of 3D printer, they can encounter issues that may require troubleshooting. Here are some common wax-based 3D printer issues and troubleshooting tips:
● Printer errors or malfunctions: Wax-based 3D printers can experience errors or malfunctions, such as failed motors, sensors, or electronics. Check for any error messages, flashing lights, or abnormal noises.
Refer to the printer's user manual or manufacturer's support for troubleshooting and resolving printer errors.
● Maintenance and cleaning: When last did you clean and generally maintain your wax 3D printer? Regular maintenance and cleaning of the printer's components, such as the print head, build platform, and material feed system, are important for optimal performance.
Follow the manufacturer's instructions for proper maintenance and cleaning procedures, and clean any wax residue or debris from the printer's components regularly.
● Failed or incomplete prints: Wax prints may fail or be incomplete due to various reasons, such as incorrect print settings, insufficient wax material, power outages, or issues with the printer's hardware.
Check and adjust the print settings, wax material level, and printer hardware, such as the print head, to ensure optimal print quality. Consider using high-quality wax material and optimizing print settings to reduce print failures and investing in a good UPS to prevent premature power outages.
● Print artifacts: Wax prints may have artifacts, such as layer lines, rough surfaces, or uneven details, which can affect the overall print quality. Adjust print orientation, print speed, and support settings to minimize artifacts.
Consider using a higher-quality wax material and optimizing print settings to reduce print artifacts.
● Print not adhering to the build platform: Proper adhesion of the wax print to the build platform is crucial for successful printing.
Ensure that the build platform is clean and level. Use a compatible wax-compatible build platform adhesive, such as wax-compatible glue or adhesive sheet, to improve adhesion. Adjust the build platform height and leveling to ensure proper first-layer adhesion.
Pro tip: Wax-based 3D printers typically use high-temperature materials and may involve heated components, so it's important to take proper safety precautions.
Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves and goggles, when handling hot or melted wax material. Follow the manufacturer's instructions for proper handling, storage, and disposal of wax materials and other printer materials.
Avoid skin contact and ingestion of wax material, and properly clean up any spills or wax residue.
All in All,
It’s no secret that you’ll certainly encounter at least one problem when working with 3D printers that’ll require troubleshooting.

From print quality problems to material issues, printer errors, and safety precautions, we have provided step-by-step troubleshooting tips to help you master the art of resolving 3D printer issues.
However, you can minimize these issues by simply getting yourself a high-quality 3D printer that is built to last. Consider visiting our webshop to get a look at our comprehensive 3D printers catalog.