3D printers get a lot of attention and for good reasons. It is impressive that a machine that looks as simple as the Aquila X2 can manufacture a complex 3D model; models that may not even be achievable using any other traditional manufacturing method. However, it is important to recognize that these machines benefit from other technologies that are just as, if not more, impressive. These include the modeling software, slicers, and crucially, the materials used for printing.

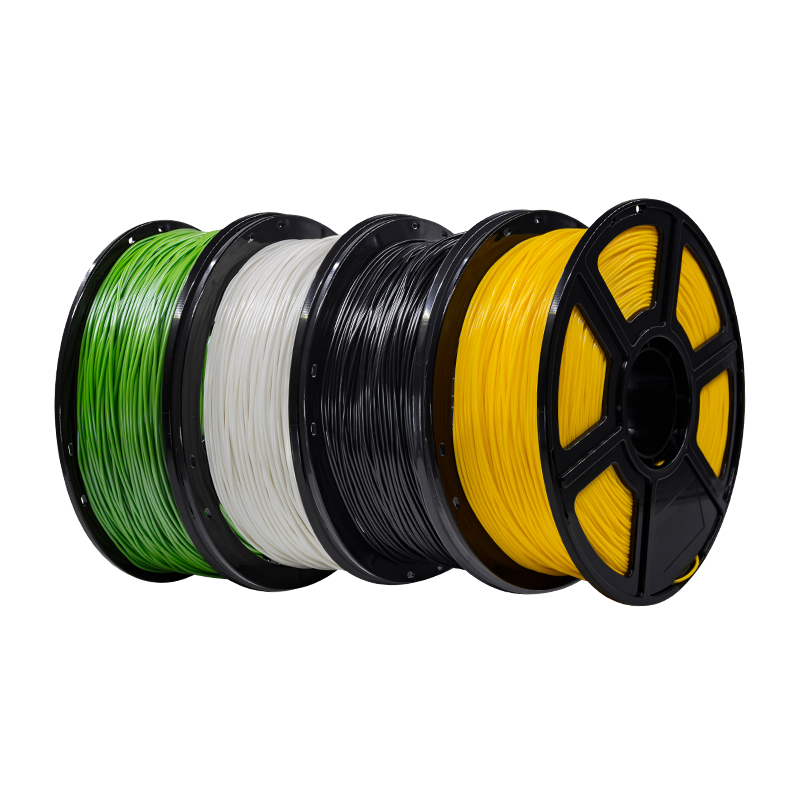
Figure 1: Only a unique range of materials can be successfully used as 3D printing materials.
Your 3D printing material is not just a random roll of plastic. For it to qualify for the job, it had to tick a lot of boxes.
The first requirement that a 3D printing material must meet is that it must be printable. This may sound simple, but this simple fact is a major reason why some commonly used plastics are not yet available as 3D printing materials. This fact also limits the use of some materials that are already used in 3D printing.
Thermoplastic or Thermoset
Thermoplastics are plastics that can be formed into a shape, melted, and reformed into a completely different shape many times. On the other hand, once a thermoset has hardened, it can not be melted back to its original shape because the hardening process is a chemical one.
ABS 3D printing material, PLA, PETG, PP, Nylon, PC, and most others you’ll find being used in FDM 3D printing are thermoplastics. The use of thermosets in FDM 3D printing is unheard of because the process doesn’t support the conditions needed to harden thermosets. Additionally, many thermosets start off as viscous liquids and there’s simply no way of pouring that down your Finder 3’s extruder without causing irreversible damage.
The hardening of a thermoset is called curing, and this is what is seen in resin 3D printing. The thermosetting resin is initially cured inside a resin 3D printer like the Foto 9.25 before the final curing takes place under UV light.
Ease of Printing
If too much effort is needed to attain a good result, this can significantly undercut any potential benefits of that result. This is an issue that is commonly witnessed when working with 3D printing materials. For example, getting a good 3D printing result when working with a soft 3D printing material is a lot more challenging compared to when using ABS 3D printing material or PLA. Even experienced makers have issues getting consistently good results when printing using materials that are naturally soft.

Figure 2: 3D Printing soft or flexible materials is quite challenging despite their usefulness.
One of the reasons why PLA is considered the main 3D printing material is down to the fact that getting good results with PLA is as easy as it gets. You don’t need an extruder that gets very hot, nor do you need a heated bed. You don’t need an enclosure, which is almost necessary when printing something like polypropylene (PP). Compared to a soft 3D printing material, the risk of extruder jams is much lower. Materials such as polycarbonate, despite their many advantages over PLA, have barely made a dent in the 3D printing market because they are not as easy to print.
Ease of Manufacturing
Another reason why a material may not be as common in the 3D printing space is the ease of manufacturing the filament. To get your 3D printing material as a filament, pellets of the same plastic are fed through an extruder and rolled onto the spools. However, this process can be more challenging depending on the material you’re working with. A high temperature 3D printing material may need other substances mixed in with the polymer. A material that absorbs moisture rapidly may require very precise process control and a controlled extrusion environment. A soft 3D printing material may need rapid cooling or a slower extrusion speed.
Many of the material-specific issues you notice when printing can also be a factor during the manufacture of the filament. If it’s too expensive to manufacture the filament, a manufacturer will not want to invest in the process unless the demand is available.
Safety
A good 3D printing material should be safe. At the very least, it should only pose risks that can be easily mitigated by the end user. Some plastics may be printable, but they may not be safe for 3D printing. Materials like ABS and ASA are considered safe for 3D printing, however, there are still concerns raised about the fumes produced when printing using these materials. This is why manufacturers like Flashforge now have printers like the Adventurer 4 which come equipped with HEPA air filters.

Figure 3: 3D printing materials must be safe to print and use because they're used by children as well.
Safety is an important factor in 3D printing materials because these machines are used for educational purposes and in homes too. This means even young children may be exposed to any harmful chemicals that are released by the machines.
In Conclusion
It takes a special type of material for you to end up with a roll of filament or a bottle of resin in your hands. A good 3D printing material is the result of a lot of science and research and their special quality should not be overlooked.