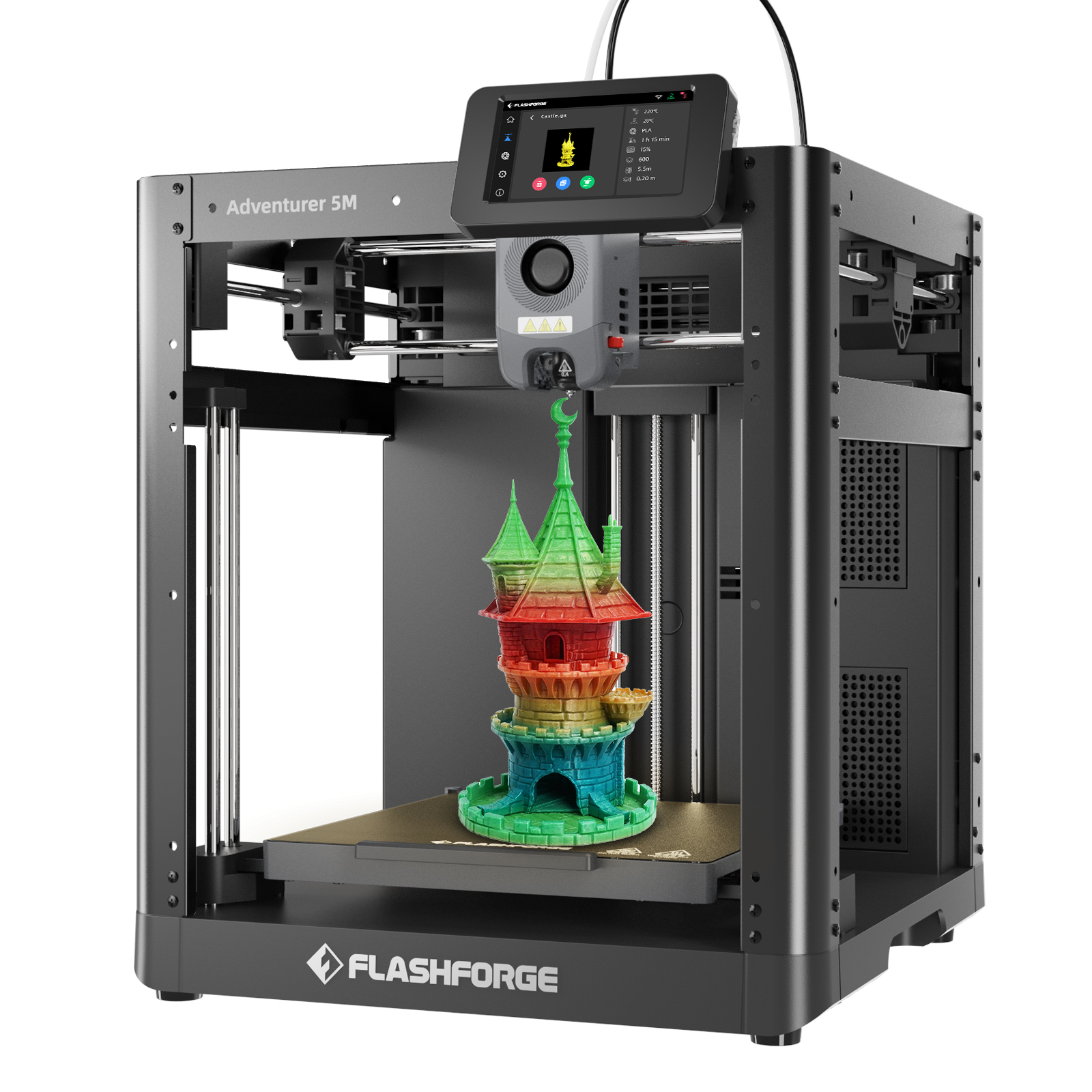
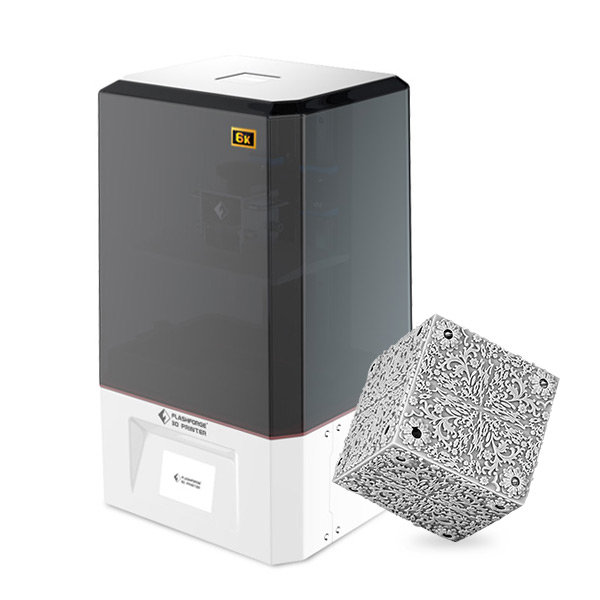
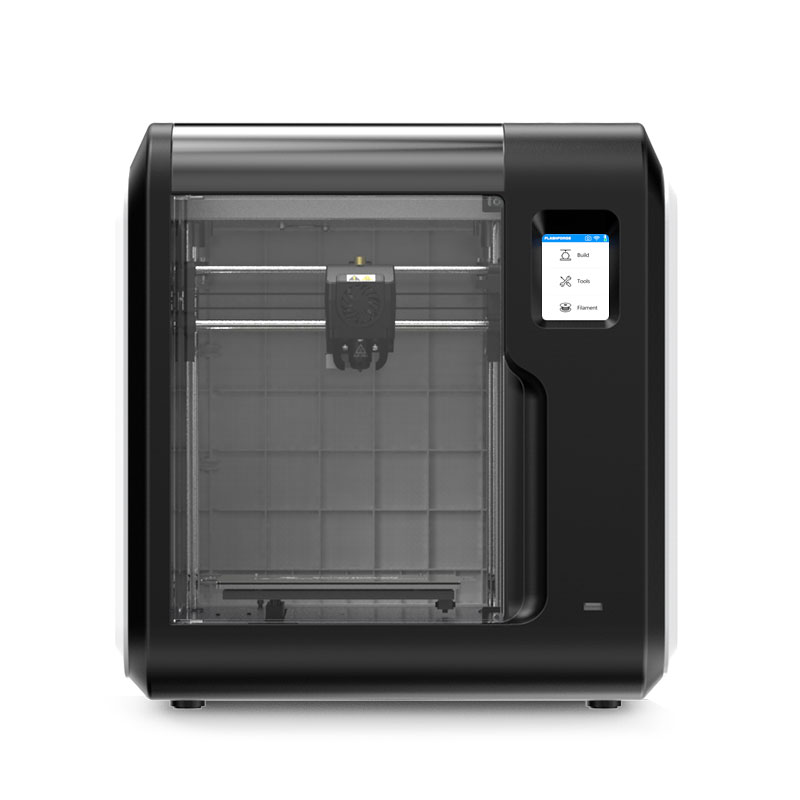
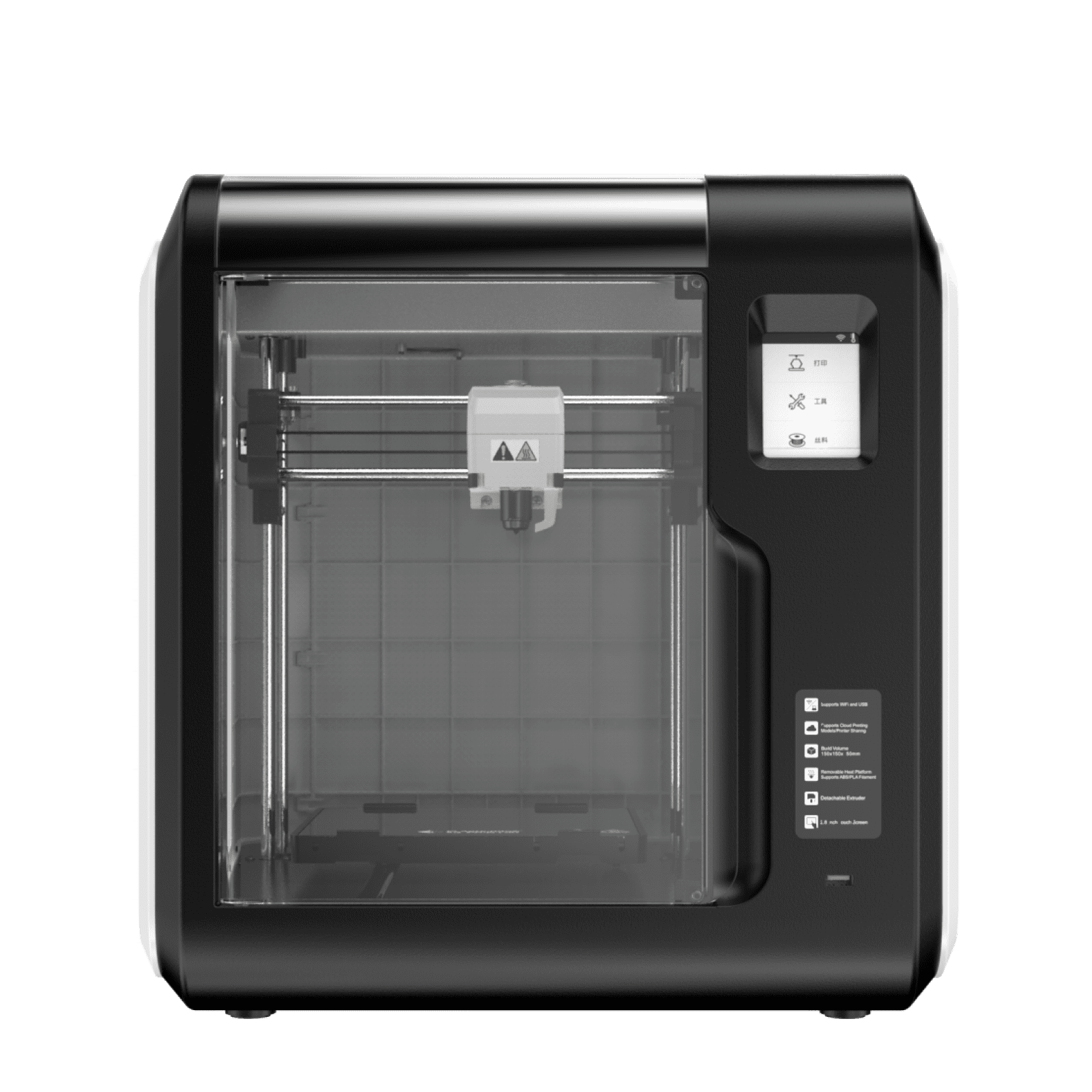
There are few materials that are as regularly associated with 3D printing as PLA. PLA filament caught on quite early as a 3D printing material. This could be due to its availability, renewable source, or the fact that it is one of the easiest materials to print with. Almost any 3D printer can produce decent prints when coupled with standard PLA.
However, PLA is no magic bullet. There are certain PLA filament properties that make it unsuitable for some applications. Therefore, it’s important to know when you shouldn’t be using PLA for 3D printing.
Properties of PLA
The technical properties of PLA would not be easy for a typical maker to understand or contextualize. It is easier to look at it in terms of advantages and disadvantages of PLA. The properties of this material can be summarized as follows:

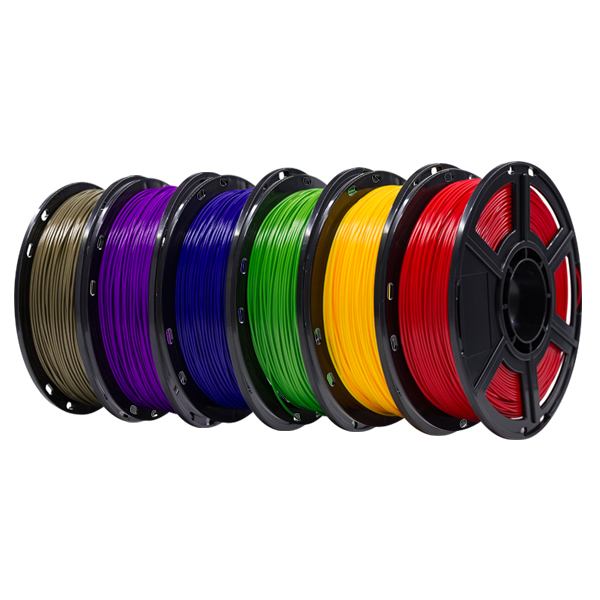
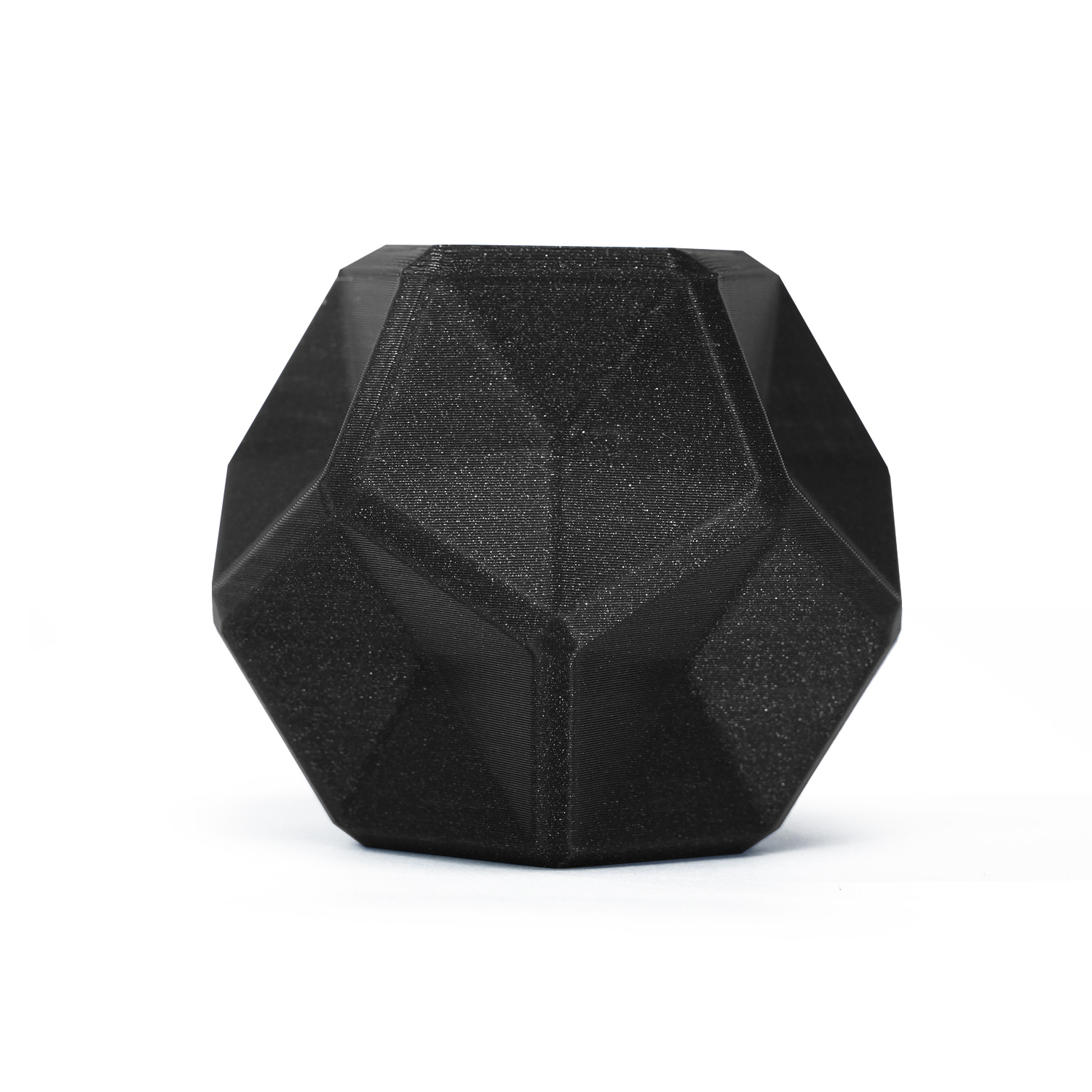
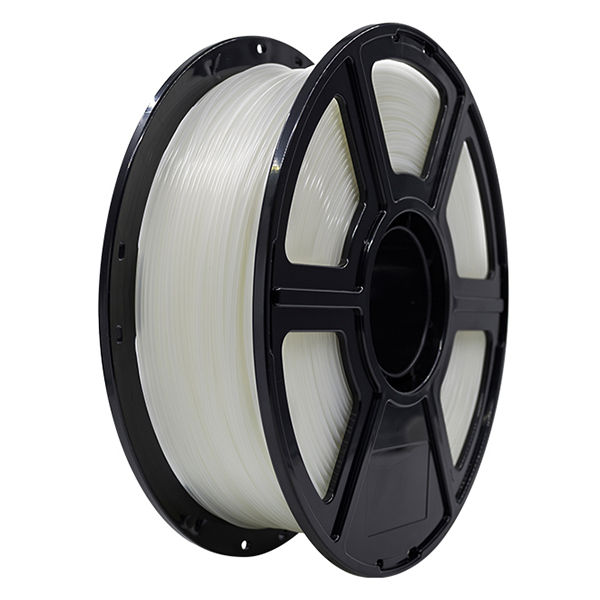
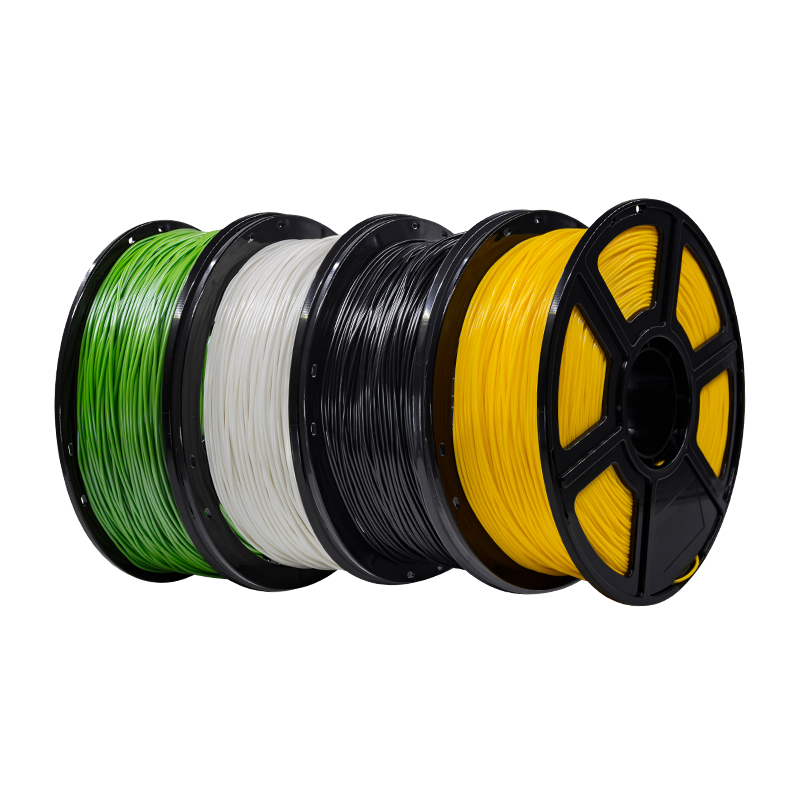
Figure 1: Almost any printer will get good results when printing using PLA.
- Ease of printing: PLA doesn’t require very high printing temperatures. Even inexpensive printers meant for education purposes will have nozzles that get hot enough to print PLA filament. It doesn’t require a heated print bed, although some prints may benefit from one. The material can also be printed at a relatively high speed, and without an enclosure.
- Cost: Initially, PLA filament prices stood out as being low compared to other material prices. However, the cost of other filament types has dropped as well in recent years. You can now get PETG filaments at comparable prices to PLA.
- Health and environmental friendliness: PLA is considered to be non-toxic and is even used for packaging food and for some medical implants. The filament doesn’t produce fumes during printing like ABS. The material is widely hailed as being eco-friendlier than other plastics. This is because it is made from plant starches. The challenge with PLA is that it is still not as biodegradable as many hoped it would be.
- Strength: The strength of PLA is not that impressive. It has low flexural strength compared to other 3D printing materials such as PETG and ABS. It’s brittle and will fail with little warning.
- Chemical and Temperature Resistance: Some chemicals will cause PLA to release lactic acid. This can be dangerous in certain quantities. The low glass-transition temperature of this material means it won’t retain its shape when subjected to heat. PLA also can’t survive very long outdoors due to its poor UV resistance.
PLA Filament Types
Due to its enduring presence in the 3D printing scene, manufacturers like Flashforge have had plenty of time to test and tweak different variations of this material. Today, the best PLA filament will likely be a blend of the material with something else. This is usually done to improve its aesthetic properties or mechanical strength. Examples of PLA types you’ll find in the market include:
- Standard PLA: This is base PLA, and it has no special features. The properties of this type of PLA should be comparable between manufacturers but there tend to be variations.
- PLA Pro: Many manufacturers will have a pro or plus variant of their standard PLA. This type of PLA usually has improved mechanical properties, e.g., higher flexural strength.
- Silk: The silk PLA option is usually targeted at makers who prioritize aesthetics, for instance, if you’re printing decorative pieces.
- Carbon fiber: The carbon fiber-infused PLA is one of the best PLA filament options you’ll find in the market today. The addition of carbon fiber can improve properties like rigidity, strength, and durability of the material.

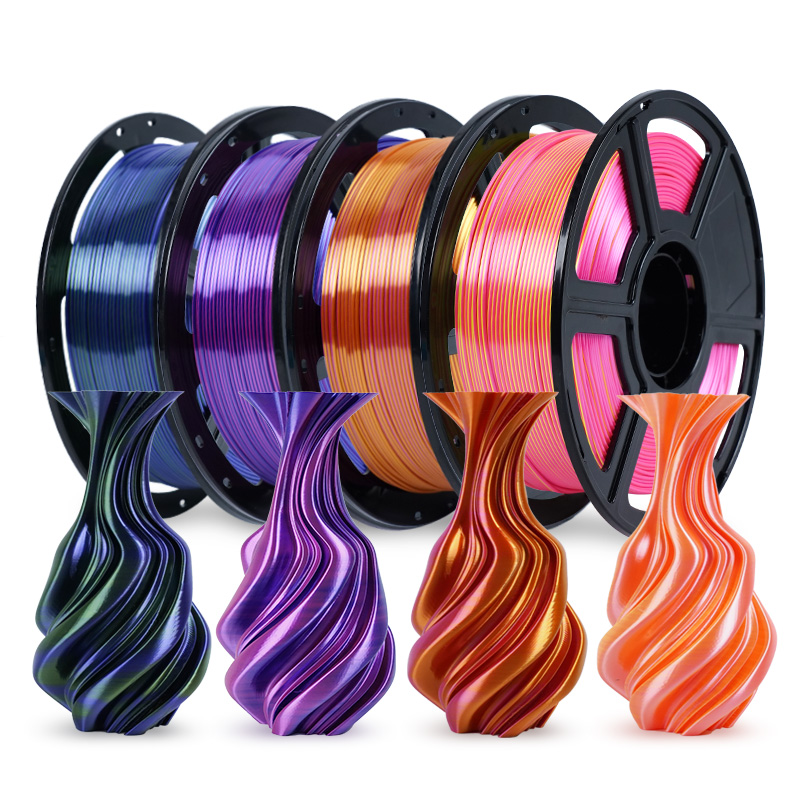
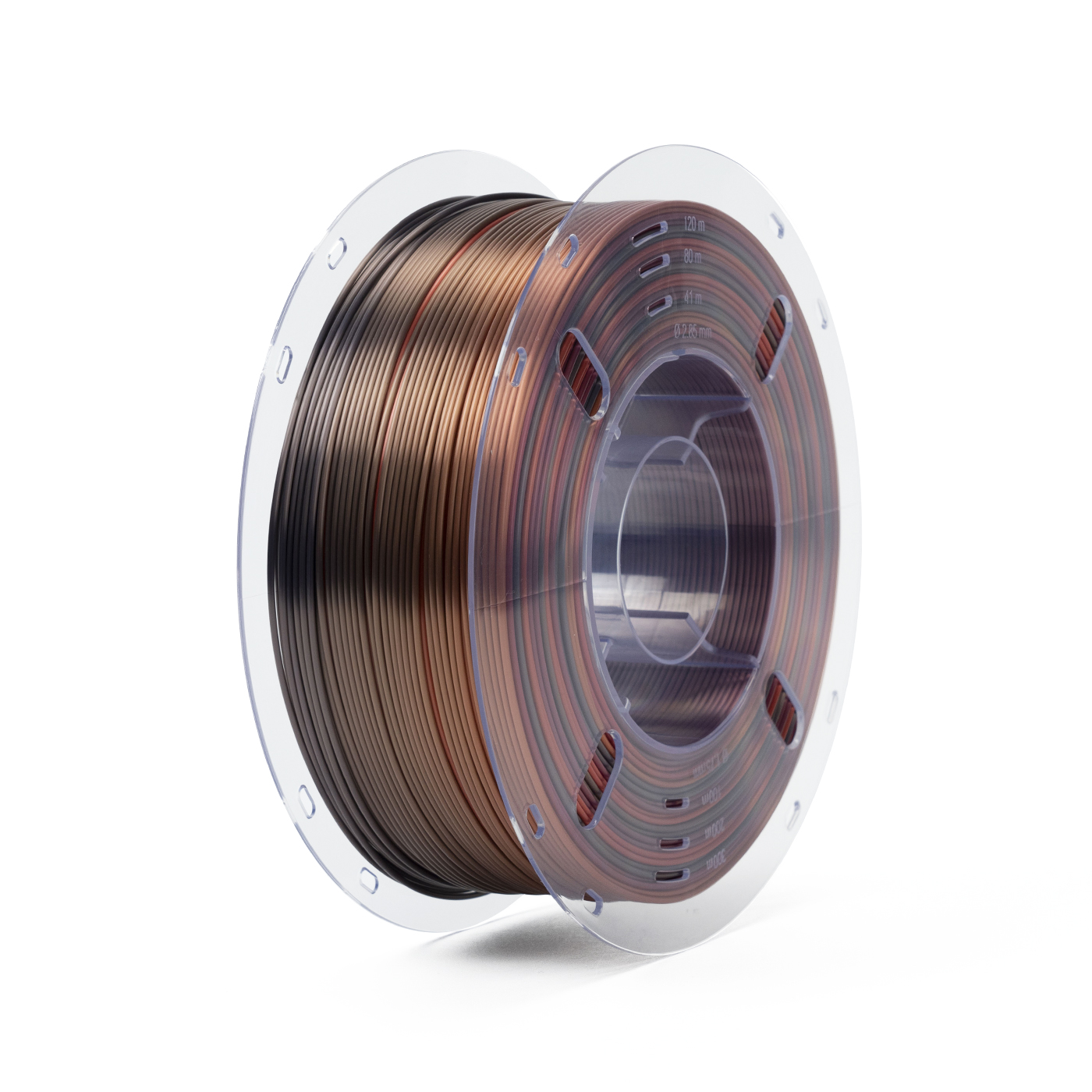
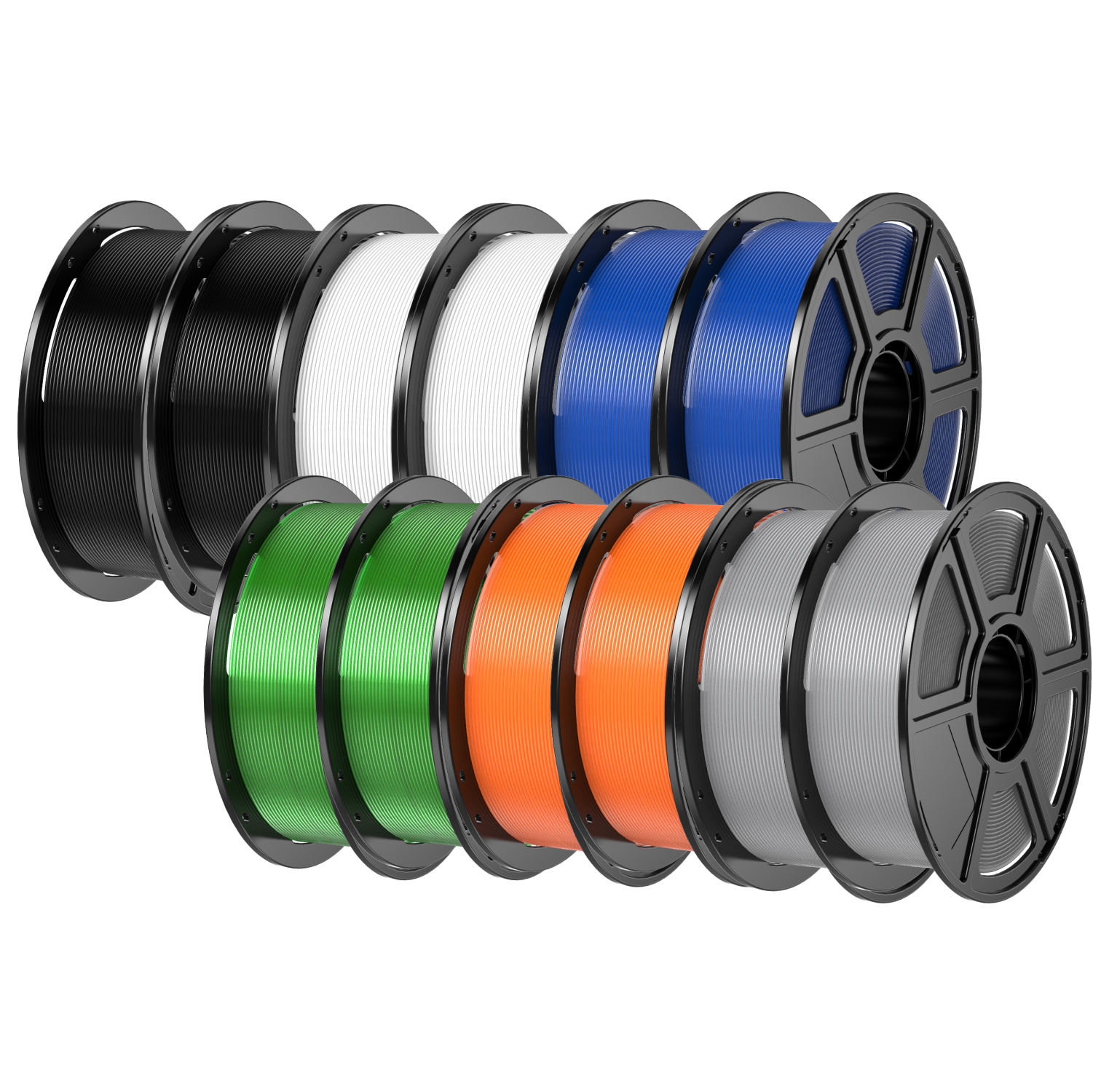
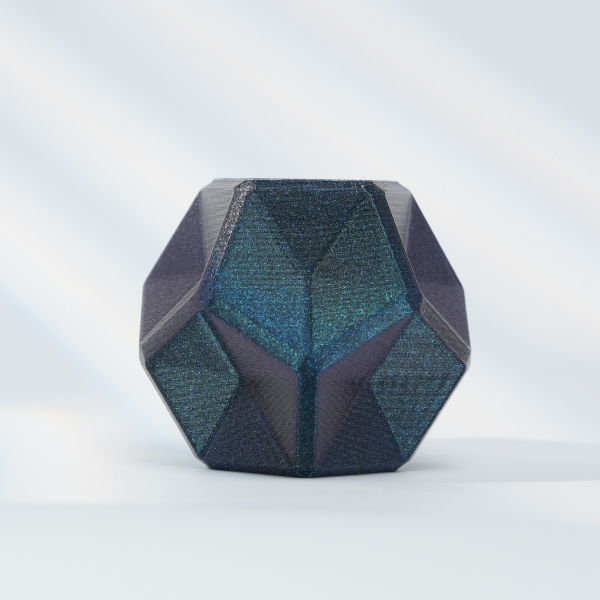
Figure 2: Special blends of PLA are needed to achieve this shiny multi-colored look.
There are many other PLA filament options available including options that glow in the dark or those featuring multiple colors. Many of these are aesthetic options and don’t improve the other PLA filament properties. Luckily, PLA filament price for the variants isn’t that much higher than that of standard PLA.
When to Use PLA
Material selection is an important part of being a maker. Choosing the wrong material for your project could easily result in failure and a waste of money. If you have some PLA lying around, it will be best used for:
- Low-strength applications: PLA’s relatively low strength means there are better options if you need something to take on some forces. Luckily, there are plenty of applications where the print will not be subjected to any force such as printing miniatures.
- Prototyping: Prototyping requires a material that can be printed quickly and easily and that is what PLA is good at. PLA is especially good at this if multiple variations of the prototype will be needed quickly.
- Products for indoor use: Not even the best PLA filament should be used if the print will be exposed to direct sunlight. Such a print will fail very quickly due to UV degradation.
- Tight tolerances: PLA filament prints well because it barely changes in size and shape after printing. Therefore, this material can be very good for prints with tight tolerances that require dimensional stability.

Figure 3: Parts that fit together are good candidates for PLA printing due to tight tolerances.